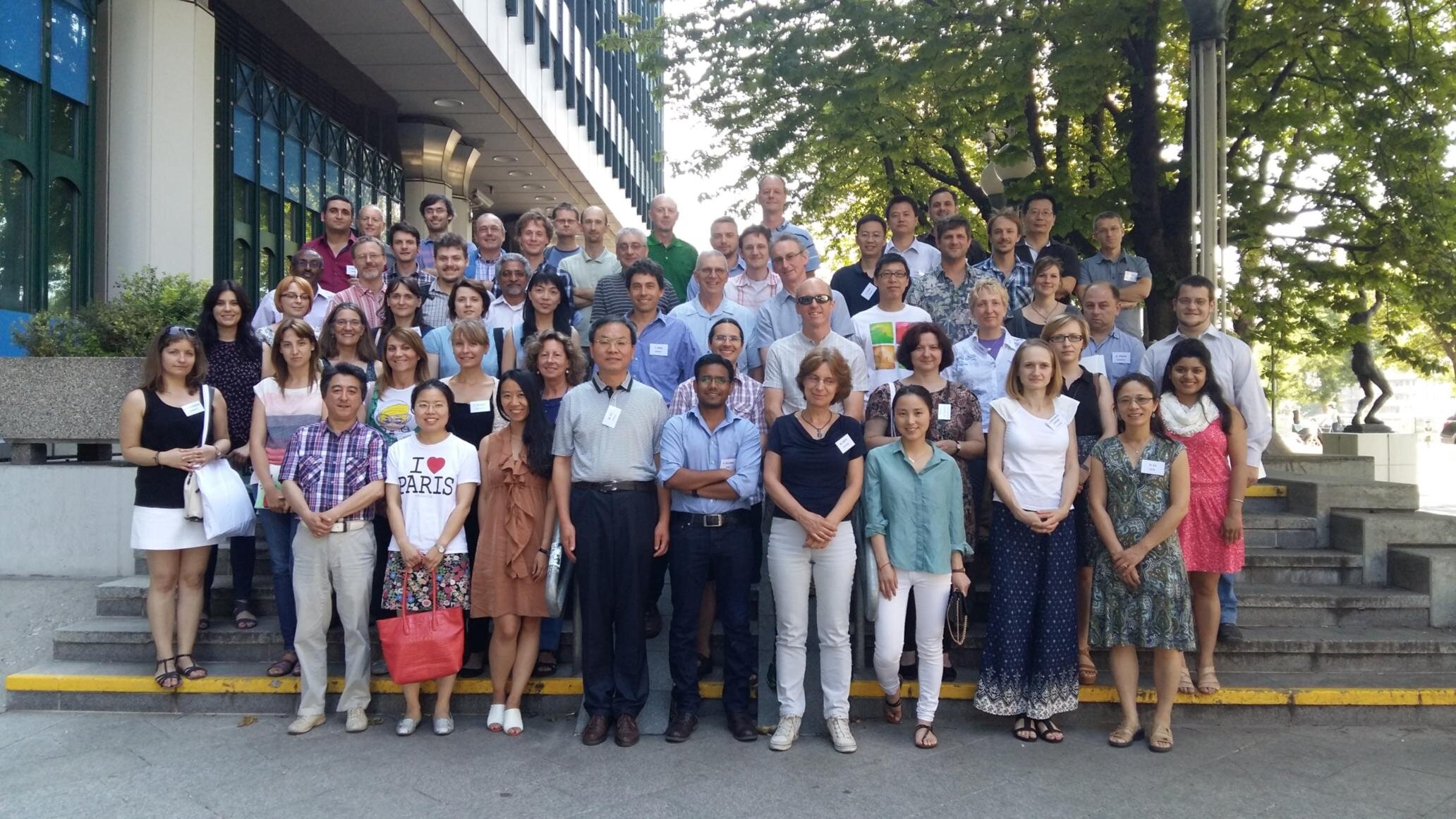
In the group of Prof. Cathrine Lillo (Stavanger, Norway)
1- Protein phosphatase 2A regulatory subunits affecting plant innate immunity, energy metabolism, and flowering time – joint functions among B'η subfamily members
Protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) is a heterotrimeric complex comprising a catalytic, scaffolding, and regulatory subunit. The regulatory subunits are essential for substrate specificity and localization of the complex and are classified into B/B55, B', and B” non-related families in higher plants. In Arabidopsis thaliana, the close paralogs B'η, B'θ, B'γ, and B'ζ were further classified into a subfamily of B' called B'η. Here we present results that consolidate the evidence for a role of the B'η subfamily in regulation of innate immunity, energy metabolism and flowering time. Proliferation of the virulent Pseudomonas syringae in B'θ knockout mutant decreased in comparison with wild type plants. Additionally, B'θ knockout plants were delayed in flowering, and this phenotype was supported by high expression of FLC (FLOWERING LOCUS C). B'ζ knockout seedlings showed growth retardation on sucrose-free medium, indicating a role for B'ζ in energy metabolism. This work provides insight into functions of the B'η subfamily members, highlighting their regulation of shared physiological traits while localizing to distinct cellular compartments.
2- Protein Phosphatase 2A Holoenzyme Is Targeted to Peroxisomes by Piggybacking and Positively Affects Peroxisomal β-Oxidation
The eukaryotic, highly conserved serine (Ser)/threonine-specific protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) functions as a heterotrimeric complex composed of a catalytic (C), scaffolding (A), and regulatory (B) subunit. In Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), five, three, and 17 genes encode different C, A, and B subunits, respectively. We previously found that a B subunit, B′θ, localized to peroxisomes due to its C-terminal targeting signal Ser-Ser-leucine. This work shows that PP2A C2, C5, andA2 subunits interact and colocalize with B′θ in peroxisomes. C and A subunits lack peroxisomal targeting signals, and their peroxisomal import depends on B′θ and appears to occur by piggybacking transport. B′θ knockout mutants were impaired in peroxisomal β-oxidation as shown by developmental arrest of seedlings germinated without sucrose, accumulation of eicosenoic acid, and resistance to protoauxins indole-butyric acid and 2,4-dichlorophenoxybutyric acid. All of these observations strongly substantiate that a full PP2A complex is present in peroxisomes and positively affects β-oxidation of fatty acids and protoauxins.
Kataya, Amr Ramzy Abass; Heidari Ahootapeh, Behzad; Hagen, Lars; Kommedal, Roald; Slupphaug, Geir; Lillo, Cathrine (2015). Protein phosphatase 2A holoenzyme is targeted to peroxisomes by piggybacking and positively affects peroxisomal β-oxidation. Plant Physiology. ISSN 0032-0889. Volum 167. Hefte 2. s. 493-506. DOI: 10.1104/pp.114.254409.
3- Investigating Protein Phosphatase 2A Regulatory Subunits: From Subcellular Localization to Abiotic Stress Implications
Protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) is a serine/threonine-specific protein phosphatase. PP2A holoenzymes are heterotrimeric complexes comprising a catalytic (C1-5), scaffolding (A1-3), and regulatory (B) subunits. The B subunits are responsible for substrate specificity and localization of the holoenzyme complex and are classified into B55, B’, and B’’ non-related families. In Arabidopsis, 17 regulatory subunits are present that can lead to 255 possible combinations. Using our description of four B’ members localization, we identified a new function for PP2A in peroxisomal β-oxidation. We fused all the remaining B’ and B’’ subunits with a reporter protein, and their localizations are under investigation. Moreover, online gene expression tools show the upregulation of two PP2A regulatory subunits (B’ζ and B’’α) in response to salt stress. Interestingly, B’ζ is targeting mitochondria and B’’α is predicted to be mitochondrial targeted. The homozygous T-DNA insertion lines for B’ζ and B’’α in Arabidopsis were isolated. From the preliminary data, the seedlings of these mutants show resistance to high salt concentrations. This indicates a negative regulatory role for PP2A during salt stress.